Introduction to Data Models
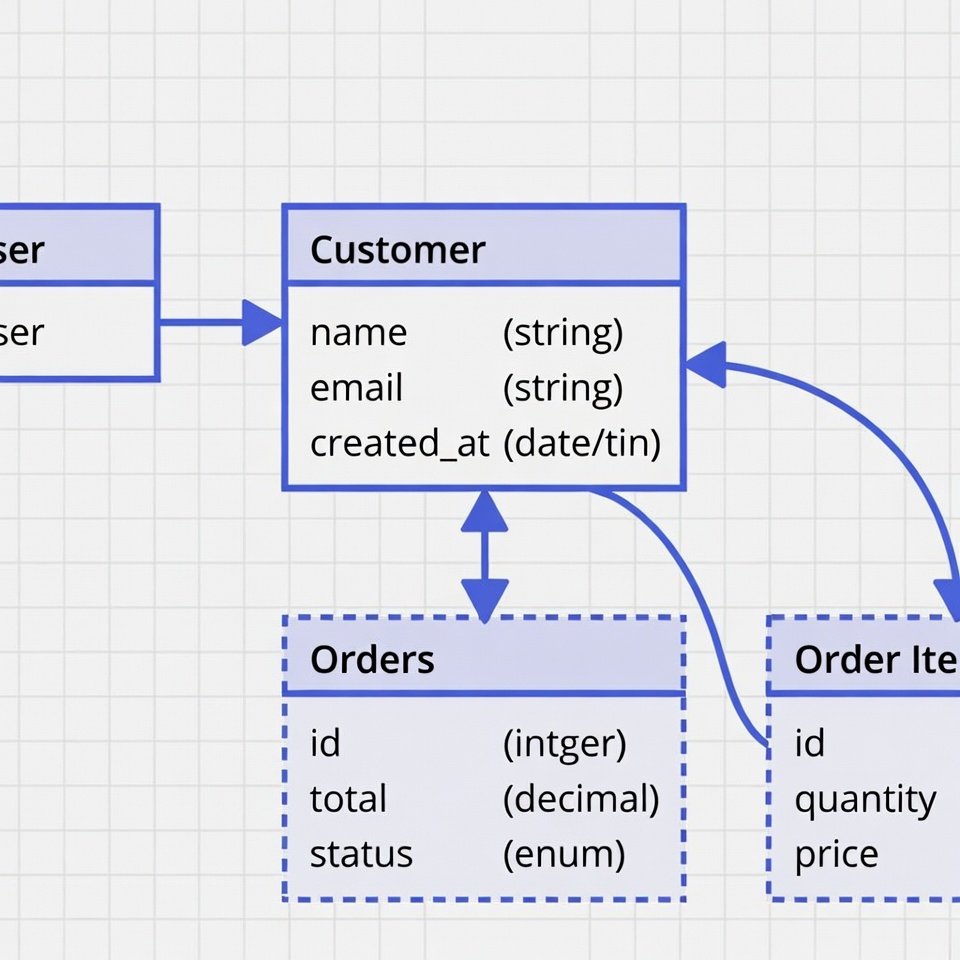
A data model serves as a foundation for managing data and enables clarity in understanding the connections and relationships between different data elements. At its core, a data model is an abstract representation of the data that is used in systems and applications, encapsulating not only the data itself but also the constraints and rules that govern its structure and manipulation. Organizations utilize data models to depict how data is stored, organized, and accessed, making them integral to effective data management practices.
The purpose of a data model extends beyond mere representation; it establishes a framework for data analysis and development. It acts as a blueprint that guides the design of databases and informs the development of applications that rely on data. This preliminary stage is essential because it helps stakeholders understand the implications of data architecture within their specific contexts, ensuring that everyone has aligned expectations and a clear understanding of how the data will be utilized.
In the realm of data management, employing a data model enables organizations to streamline processes, enhance data quality, and promote data consistency. By structuring information logically, data models aid in identifying redundancies and gaps in data flows. Furthermore, they provide a means for data integration, allowing disparate systems to interoperate effectively. Consequently, organizations can leverage these models to improve decision-making, foster data-driven strategies, and ultimately drive better business outcomes.
In summary, data models are pivotal as they not only provide an abstract representation of data but also simplify the complexities involved in data management. A well-structured data model contributes significantly to an organization’s ability to understand and utilize its data effectively in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Types of Data Models
Data models serve as essential frameworks for structuring data in a manner that can be understood and manipulated effectively. In the realm of data analysis and development, three primary types of data models are widely utilized: conceptual, logical, and physical data models.
The conceptual data model focuses on defining the high-level structure of information within a system, outlining what data is essential and how different entities relate to one another. This model serves as a blueprint for the entire data landscape and is often non-technical, making it accessible to stakeholders who may not have a deep understanding of database functions. The emphasis here is on identifying key concepts and entities without delving into the complexities of software implementation or data management.
Logical data models, on the other hand, build upon the conceptual framework by incorporating more details about how data elements interconnect. This model remains independent of physical implementation, meaning that it does not concern itself with how data will be stored or accessed. Instead, a logical data model focuses on the organization of data—defining attributes, identifiers, and relationships among entities. This type is vital as it serves as a bridge between the high-level conceptual overview and the more technically-focused physical model.
Lastly, the physical data model represents the actual implementation of the data structure in a database management system. This model outlines how data is stored, the data types being used, and the specific architecture of the database. It accounts for performance, indexing, and the physical storage of data, providing a clear guide for developers and database administrators on how the data will reside on storage media.
By understanding these three types of data models—conceptual, logical, and physical—organizations can effectively design their data architecture, which is critical in data analysis and development endeavors.
The Importance of Data Models in Analysis
Data models play a pivotal role in the realm of data analysis by providing a structured framework that assists analysts in interpreting complex datasets. A well-structured data model not only visualizes data but also enhances the understanding of trends, relationships, and patterns inherent within the data. This visualization is critical, as it enables analysts to discern insights that may otherwise remain obscured in raw data formats.
One of the primary functions of a data model is to establish a clear representation of the data environment, which facilitates better decision-making. For instance, by employing entity-relationship diagrams (ERDs), analysts can illustrate how various data entities interact with one another. This clarity aids in identifying correlations and causations, ultimately empowering stakeholders to make informed choices based on data-driven insights. Furthermore, data models can significantly reduce ambiguity by providing common terminology and standardized formats that analysts can refer to throughout their processes.
Moreover, data models also enhance the effectiveness of data analysis by highlighting critical metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators). For example, in retail analysis, models can be constructed to track customer purchasing behavior over time. Such insights might reveal trends like seasonal purchasing spikes or shifts in consumer preferences. These findings are indispensable for developing strategies aligned with market demands and improving overall business performance.
In conclusion, data models are integral to the data analysis process. By structuring information in a visually interpretable manner, they foster a deeper understanding of data relationships and patterns, thereby supporting analysts in making strategic, informed decisions based on comprehensive insights derived from the data.
Data Modeling Techniques
Data modeling is an essential aspect of data analysis and development, providing a structured framework that facilitates data management, integration, and accessibility. Various data modeling techniques are employed by data professionals, each offering distinct advantages depending on the context in which they are applied.
One widely used technique is the Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD). ERDs visually represent data entities and their interrelationships, making it easier to comprehend complex data structures. This technique is particularly beneficial during the initial phases of database design, as it aids in identifying entities, attributes, and the connections between them. By doing so, developers can effectively create databases that are structured and scalable.
Another valuable tool is the Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram. UML diagrams are versatile and can be adapted to a range of scenarios. They provide a standardized way to visualize the architecture of systems, showcasing not only data entities but also processes and behaviors. UML is especially useful in software engineering contexts, as it assists in bridging the gap between data models and functional elements of software applications.
Data flow diagrams (DFDs) serve another purpose by focusing on how data moves through a system. DFDs allow data professionals to visualize the flow of information, illustrating inputs, outputs, and the processes that transform data. This technique is most effective in situations where understanding the flow of data is crucial for optimizing processes, identifying bottlenecks, or ensuring data integrity.
In conclusion, the choice of data modeling technique should be guided by the specific requirements of the project at hand. By leveraging ERDs, UML diagrams, and DFDs, data professionals can enhance their ability to analyze and develop systems that effectively meet organizational needs.
Data Models in Software Development
Data models serve a pivotal role in the software development lifecycle, influencing how developers approach the design and implementation of applications. At the core of this influence is the ability to create a structured framework that effectively represents data relationships, enabling developers to build efficient and robust databases frequently utilized within application architectures.
When engaging in software development, developers often start by utilizing data models to conceptualize the necessary data structure of their applications. This process includes defining entities and their relationships, which is critical for ensuring that the data can be accurately represented and manipulated within the application. For instance, through tools such as Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs), developers can visualize how different entities interact, which helps in organizing and implementing the database schema effectively.
In addition to aiding in database design, data models also guide the creation of backend architectures. By establishing clear data workflows, developers can ensure that their applications manage data efficiently, retrieve it quickly, and maintain its integrity throughout various operations. This structured approach to data management enhances overall application performance and user experience. Moreover, it provides a blueprint for integrating new features or modifying existing ones, allowing for greater adaptability as software requirements evolve.
Furthermore, adherence to well-defined data models contributes significantly to consistency and accuracy in data-driven applications. When developers implement these models, they can minimize the likelihood of errors associated with data mismanagement, thereby promoting a more seamless user experience and effectively meeting project requirements.
Best Practices for Creating Data Models
Creating effective data models is essential for any organization aiming to leverage data effectively in decision-making. To achieve this, certain best practices should be adhered to ensure clarity, normalization, and stakeholder engagement in the modeling process.
Firstly, clarity is paramount. A well-defined data model should be straightforward, allowing both technical and non-technical users to understand the structure and relationships within the data. This involves using intuitive naming conventions and keenly documenting the purpose of each entity and relationship. Aim for a design that intuitively communicates its intent, facilitating smoother communication across teams.
Next, normalization is a critical component in the integrity of data models. Normalization refers to the process of organizing data to minimize redundancy and dependency, which can simplify data maintenance and improve query performance. Strive to reduce issues such as update anomalies, which can occur when multiple data storage points hold the same information. Implementing effective normalization practices enhances the consistency and reliability of the model.
It is also crucial to involve stakeholders throughout the modeling process. Engaging users who will interact with the data model provides invaluable insights and feedback, which can lead to better alignment with business needs. Regularly scheduled reviews and revisions with team members ensure that their perspectives are considered, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of requirements and expected outcomes.
Lastly, the iterative process of developing a data model should be embraced, allowing for ongoing refinements as new requirements emerge or as business landscapes change. By following these best practices, organizations can create data models that are not only robust and accurate but also serve as foundational elements for successful data analysis and application development.
Challenges in Data Modeling
Data modeling plays a crucial role in data analysis and development, yet practitioners often encounter a variety of challenges. One prominent issue is the evolving nature of business requirements. As organizations strive to adapt to market dynamics, stakeholder expectations may shift, leading to discrepancies between initial data models and the actual needs of the business. This can result in models that fail to accurately represent the current operational landscape, making it imperative for data professionals to remain agile and flexible.
Another challenge is data quality. Inconsistent, incomplete, or inaccurate data can significantly hinder the effectiveness of any data model. Poor data quality not only complicates the modeling process but can also lead to misleading insights during analysis. It is essential to implement robust data governance practices to ensure that data integrity is maintained throughout the modeling lifecycle. Regular data audits and validation processes can help identify and rectify quality issues at an early stage.
Integration complexities also pose substantial hurdles in the data modeling field. Organizations often aggregate data from multiple sources, which can lead to compatibility issues and hinder the creation of a coherent data model. To address this, organizations should invest in standardized data integration tools and technologies that facilitate seamless synchronization across various platforms. These tools can help harmonize disparate data sets, thus enabling more efficient data modeling processes.
In order to mitigate these challenges, collaboration among stakeholders is essential. Regular communication can help align business objectives with data modeling efforts, ensuring that the model remains relevant and functional. Moreover, adopting agile methodologies can provide the flexibility needed to adapt to changing requirements while maintaining high data quality standards.
Emerging Trends in Data Modeling
In the rapidly evolving landscape of data analysis and development, emerging trends in data modeling are significantly reshaping how organizations manage and interpret their data. One of the most notable trends is the rise of NoSQL databases, which have gained popularity due to their ability to handle vast amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data. Unlike traditional relational database management systems, NoSQL databases offer flexibility in data storage and retrieval, making them particularly well-suited for applications requiring scalability and speed.
Another major trend is the adoption of data lakes, which serve as centralized repositories for storing raw data in its native format. This approach allows organizations to capture data from various sources without the need for pre-processing, facilitating advanced analytics and machine learning applications. By leveraging data lakes, organizations can analyze large volumes of data more effectively, thereby deriving insights that were previously difficult to obtain.
Furthermore, the influence of artificial intelligence (AI) in automated data modeling is becoming increasingly prominent. AI technologies are being utilized to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of data modeling processes. Automation tools powered by machine learning algorithms can identify patterns, provide recommendations for data structuring, and even generate data models without substantial human intervention. This advancement not only streamlines workflows but also allows data analysts to focus on more strategic tasks.
These trends in data modeling are shaping the future of data analysis and development, enabling organizations to leverage their data assets more effectively. As businesses continue to embrace these innovations, the ability to harness vast and complex datasets will drive strategic decision-making and competitive advantage in various industries.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we explored the critical role of data models in both data analysis and software development. These models serve as frameworks that help in organizing and structuring data, facilitating better understanding and management. By implementing effective data modeling techniques, organizations can ensure that their data is accurate and accessible, which in turn enhances the efficiency of data-driven decision-making processes.
Throughout the article, we emphasized the significance of data models in enabling analysts and developers to visualize relationships within the data, identify trends, and derive actionable insights. The collaborative nature of data modeling not only streamlines communication between stakeholders but also enhances the overall development lifecycle. Thus, adopting robust data modeling practices can lead to an improved foundation for data management and analytics.
Empowering your data practices through the use of well-structured data models can significantly influence project outcomes. As businesses continue to rely on data for strategic initiatives, leveraging comprehensive data models is essential for achieving their objectives. We encourage our readers to reflect on their current data practices and consider how integrating effective data modeling techniques can lead to better insights and improved decision-making. The understanding of data models is not merely academic; it has real-world implications that can elevate the data-analysis processes to new heights.

