By Ankit Srivastava – Data Analytics & BI Trainer @ SlideScope
In today’s data-driven world, businesses rely on timely and accurate data to make strategic decisions. But before that data can power dashboards, AI models, or reports, it must be properly extracted, transformed, and loaded — a process we call ETL (Extract, Transform, Load).
As someone who has mentored thousands of learners in Data Analytics and Business Intelligence, I often get this question — “Ankit, how do I become an ETL Developer?”
If you’re passionate about data pipelines, database systems, and automation, then an ETL Developer role can be a perfect fit for you.
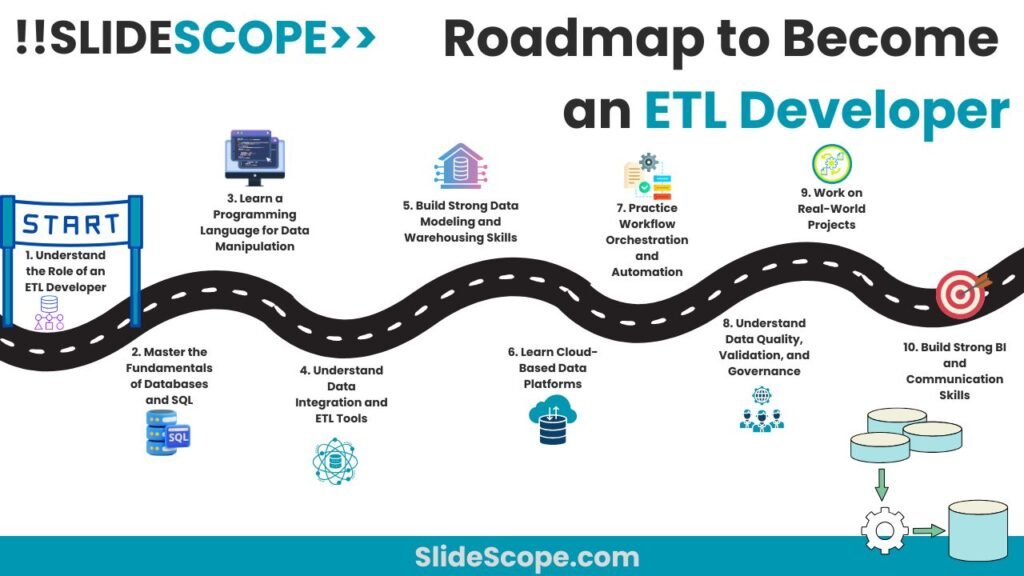
Let’s go through a 10-step roadmap to becoming an ETL Developer — with the skills, tools, and mindset you’ll need to grow in this exciting field.
1. Understand the Role of an ETL Developer
Before diving into technical tools, start by understanding what ETL really means and what problems it solves.
An ETL Developer’s primary responsibility is to build and maintain systems that move data from multiple sources (databases, APIs, cloud apps, etc.) to data warehouses or analytics systems. You ensure the data is clean, accurate, and optimized for reporting.
In short, you make raw data usable.
Key responsibilities include:
- Extracting data from diverse sources
- Transforming data (cleaning, standardizing, enriching)
- Loading it into target systems such as Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift, or SQL Server
- Automating and scheduling ETL pipelines
- Ensuring data integrity and performance
If you understand the why behind ETL, the technical part becomes much easier.
2. Master the Fundamentals of Databases and SQL
Every ETL Developer must be fluent in SQL — it’s your most essential language.
Learn to:
- Write complex joins, subqueries, and aggregations
- Optimize SQL queries for performance
- Understand indexes, normalization, and schema design
- Work with both OLTP (transactional) and OLAP (analytical) databases
Practice with:
- MySQL or PostgreSQL for relational basics
- SQL Server or Oracle for enterprise features
- Explore how SQL integrates with ETL tools
Also, learn basic data warehousing concepts like Star Schema, Snowflake Schema, Fact and Dimension tables, and Surrogate Keys.
Understanding how data is stored and retrieved helps you design better ETL pipelines.
3. Learn a Programming Language for Data Manipulation
ETL often requires scripting beyond drag-and-drop tools.
The most popular languages are Python and Scala.
Start with Python, as it’s widely used for:
- Writing transformation logic
- Connecting to APIs
- Automating ETL jobs with libraries like Pandas, SQLAlchemy, or PySpark
Example: You can use Python to extract data from an API, clean it using Pandas, and load it into a database using a bulk insert.
Later, if you work in big data environments, learn Scala for Spark-based ETL.
But Python will take you 80% of the way.
4. Understand Data Integration and ETL Tools
Once you know the logic, it’s time to learn industry tools.
Popular ETL tools include:
- Informatica PowerCenter
- Talend Open Studio
- Microsoft SSIS (SQL Server Integration Services)
- Pentaho Data Integration (PDI)
- Apache Nifi
- AWS Glue (for cloud ETL)
- Apache Airflow (for orchestration and automation)
If you’re starting out, I recommend Talend or SSIS. They have great documentation, strong community support, and free versions.
Focus on learning:
- How to connect multiple data sources
- Data flow design
- Error handling and logging
- Scheduling and dependency management
An ETL tool is just a framework — your logic and understanding of data flow matter most.
5. Build Strong Data Modeling and Warehousing Skills
ETL Developers work closely with Data Engineers and BI Developers to create structured data models.
Learn how to:
- Design Fact and Dimension tables
- Implement slowly changing dimensions (SCD)
- Create efficient schema designs for reporting tools like Power BI, Tableau, or Looker
- Handle incremental loads, historical tracking, and data versioning
For hands-on practice:
- Design a small Sales or Hospital Management data warehouse
- Build ETL pipelines to populate it
- Connect it to Power BI for visualization
This real-world practice strengthens your end-to-end understanding.
6. Learn Cloud-Based Data Platforms
Modern ETL workflows increasingly use cloud data platforms instead of on-premise systems.
Some of the most in-demand tools are:
- Amazon Redshift
- Google BigQuery
- Azure Synapse Analytics
- Snowflake
Learn how to connect ETL tools or Python scripts to these cloud warehouses.
Also, get familiar with cloud storage services:
- AWS S3
- Azure Blob Storage
- Google Cloud Storage
These services are often used as staging layers for large ETL operations.
If you can deploy and automate ETL pipelines on the cloud, you’re already ahead of most beginners.
7. Practice Workflow Orchestration and Automation
Building one ETL pipeline is great, but in real projects, you’ll manage hundreds.
That’s where workflow orchestration tools like Apache Airflow, AWS Glue Workflows, or Azure Data Factory Pipelines come in.
Learn how to:
- Schedule ETL jobs
- Define dependencies (e.g., run Job B only after Job A succeeds)
- Handle retries and alerts
- Monitor pipeline execution
Automation is crucial — businesses depend on fresh, reliable data every day.
ETL developers who know how to design automated pipelines become indispensable.
8. Understand Data Quality, Validation, and Governance
It’s not enough to move data — it must be accurate, consistent, and compliant.
As an ETL Developer, you must implement data validation rules such as:
- Schema checks (column types, missing fields)
- Range checks (valid dates, numeric limits)
- Referential integrity (matching IDs across tables)
- Duplicates and null handling
You’ll also work closely with data governance frameworks ensuring data privacy and compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.).
Learn to document your ETL workflows clearly.
Use tools like Great Expectations or Deequ to automate quality checks.
In short — trust in your data is what defines your success as an ETL developer.
9. Work on Real-World Projects
Nothing builds confidence like real practice.
Start with small, practical projects to simulate real business scenarios.
Here are a few examples you can build:
- Retail Sales ETL Pipeline: Extract CSVs, clean them with Python, and load into PostgreSQL.
- Hospital Management ETL: Transform patient and staff data for Power BI dashboards.
- Social Media Analytics: Fetch data via API (Twitter, YouTube), transform, and store in BigQuery.
- Financial Data Pipeline: Automate daily stock data extraction and transformation for dashboards.
Deploy these on AWS or Azure, and you’ll have a solid portfolio.
You can also upload projects on GitHub or write case studies on Medium or LinkedIn to showcase your learning.
10. Build Strong BI and Communication Skills
The final step is integration — connecting ETL outputs to Business Intelligence dashboards and explaining insights to stakeholders.
Learn tools like:
- Power BI
- Tableau
- Looker Studio
These will help you visualize and validate your ETL results.
As an ETL Developer, you should be able to say,
“This pipeline loads sales data daily, feeding the executive dashboard that tracks revenue by region.”
That’s what turns technical skills into business impact.
Finally, focus on your soft skills — communication, documentation, teamwork, and analytical thinking.
ETL Developers often collaborate with data analysts, BI engineers, and product managers, so clarity and problem-solving are key.
Final Thoughts from Ankit
Becoming an ETL Developer is not about learning one tool — it’s about mastering the data flow mindset.
You’ll move from raw, scattered data to structured insights that power business decisions.
To summarize your roadmap:
- Understand the ETL role
- Learn SQL deeply
- Master a scripting language (Python)
- Get hands-on with ETL tools
- Learn data modeling and warehousing
- Explore cloud platforms
- Automate workflows
- Ensure data quality and governance
- Build real-world projects
- Develop BI and communication skills
Keep learning, keep experimenting — and never stop being curious about data.
That curiosity is what transforms you from a beginner to a professional ETL Developer.